DISCLAIMER: Mito Red Light devices are not clinically proven to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical conditions. Mito Red Light devices are low / risk general wellness devices aimed at affecting the body through supporting cellular function. The scientific studies referenced in this article are for educational and informational purposes only and are meant to educate the reader on the exciting and growing field of phototherapy. To see a list of precautionary warnings and contraindications, click here
Medically Reviewed by | Heidi Wright, BSN, RN, PCCN
Melatonin is a crucial hormone in regulating the sleep-wake cycle and maintaining our overall health. This hormone is released into the bloodstream from the pineal gland in response to changes in light exposure and promotes the onset of better sleep.
Melatonin is also produced in our cells and does not influence or affect our circadian rhythm when it is produced in the cells and not released into the bloodstream. 95% of melatonin produced is in the cells, helping to regulate metabolism and reduce inflammation.
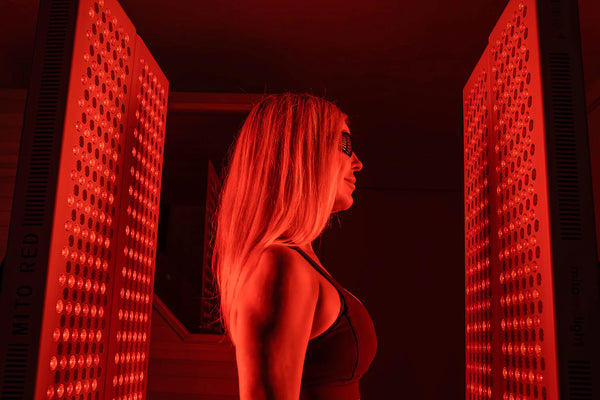
Red light therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT) or photobiomodulation, has recently gained popularity for its potential health benefits. Red light therapy is a non-invasive option that uses red and near-infrared light to potentially support cellular function and stimulate the body's natural healing processes.
Red light therapy has been found to affect melatonin secretion in the body. Studies have shown that exposure to red and near-infrared light can potentially help support healthy melatonin levels and help you get quality sleep. It is thought that red light therapy affects both melatonin released by the pineal gland and produced in the cells.
What is Red and Near-Infrared Light?
Red light and near-infrared light are part of the electromagnetic spectrum, a spectrum that includes both visible light and invisible light, like ultraviolet light and X-rays. Red light has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency of any type of visible light. Near-infrared light has a longer wavelength than red light and is not actually visible.
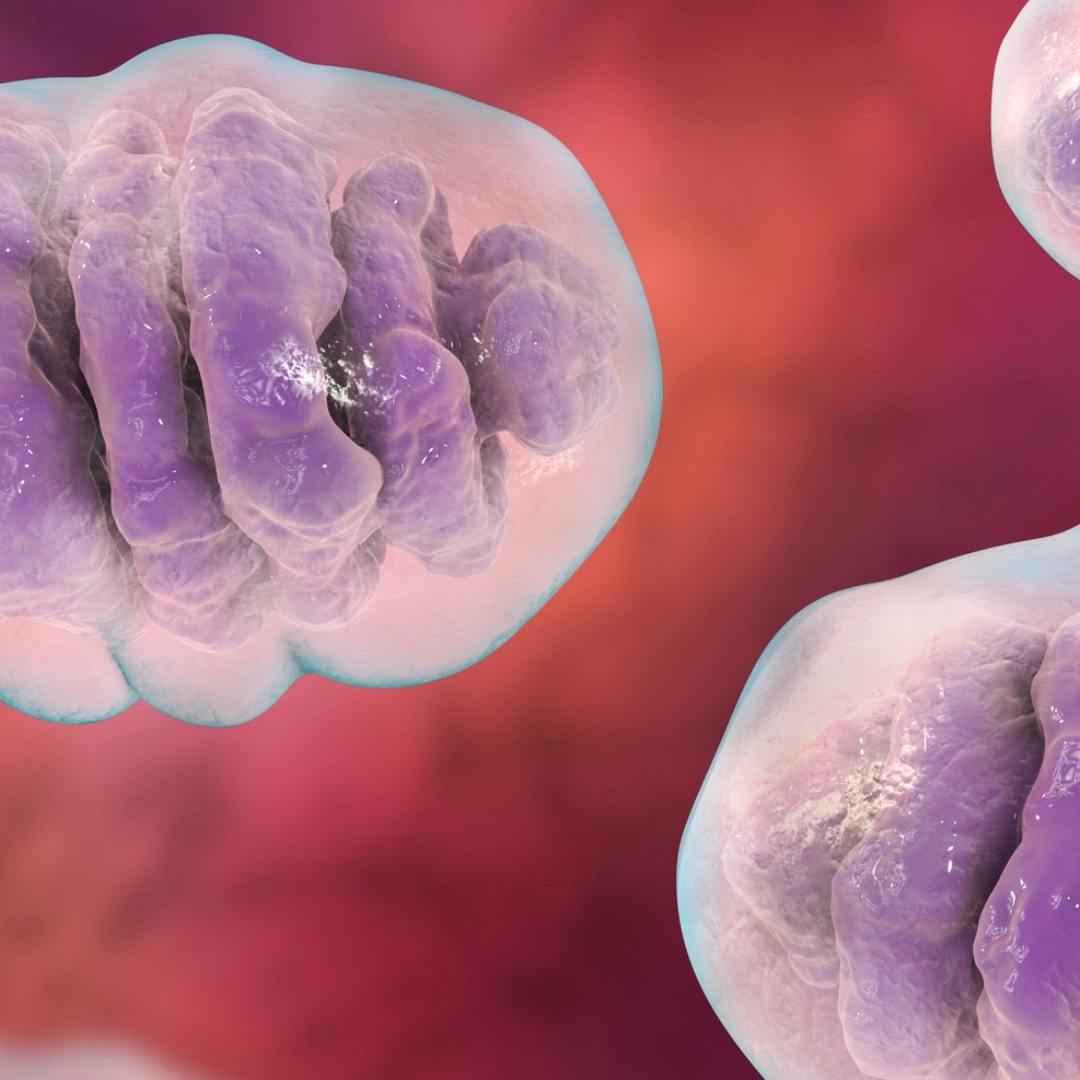
Red and near-infrared light therapy uses these specific wavelengths of light to stimulate cellular function and promote healing. They are thought to primarily work by stimulating a small organ present in most cells called the mitochondria. Mitochondria are the energy center of each cell, and stimulating the mitochondria can help support proper energy production as well as the production of cellular chemicals like melatonin.
In addition to how they affect mitochondria in a way that other types of light bulb do not, red and near-infrared light have several properties that make them ideal for treatment using light (called phototherapy). For example, they can penetrate deep into the skin and tissues, enabling them to reach a large number of cells and potentially promote the healing of deeper structures, like muscles and joints. Phototherapy using these wavelengths is also non-invasive and painless, making it a safe and effective alternative to other options. Unlike other wavelengths of light, red light and near-infrared light are not known to be connected with any major health risks and are generally regarded as largely safe.
The effectiveness of red and near-infrared light therapy depends on the dosage and timing of light exposure. In general, a longer duration of exposure and higher intensity of light is associated with better results.
In recent years, red and near-infrared light therapy has become increasingly popular as an at-home option. There are various devices available on the market, such as handheld devices, light panels, and even full-body systems, which can be used in the comfort of your own home.
However, it is important to understand that not all devices are designed for safety or quality, making it important to select the best device for your needs.
How Red and Near-Infrared Light Affect Melatonin Production
Several studies have investigated the effects of red light and near-infrared light on melatonin production, and the results are promising. One study found that red light exposure helped support proper melatonin levels in the bloodstream and led to corresponding support for sleep patterns. Another study showed that near-infrared light even helped support levels of melatonin at the cellular level, potentially augmenting the benefits of this type of method.
The mechanisms behind the effect of red and near-infrared light on melatonin production are not fully understood. It is unlikely that red light therapy directly stimulates the pineal gland, which is responsible for melatonin production. The pineal gland is located under the skull, in an area where light is unlikely to meaningfully penetrate and cause an effect.
Red and near-infrared light are thought to help support the proper activation of specific enzymes and proteins in the mitochondria, such as cytochrome C oxidase, which in turn may support the production of melatonin in the cells.
Interestingly, the effect of red and near-infrared light on melatonin production seems to be most effective in the evening, when melatonin levels are naturally rising. Exposure to blue light, such as from electronic devices, can suppress melatonin production and interfere with the effectiveness of red and near-infrared light therapy. Importantly, in the evening red light and other similar wavelengths of light are naturally present in greater amounts. Non-artificial evening light from a sunset, fire, and other forms of evening light is primarily red or orange.
Overall, the evidence suggests that red and near-infrared light therapy may be a promising option for supporting melatonin production and maintaining the body’s internal clock. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms involved.
What Are the Benefits of Red Light and Near-Infrared Light Therapy on Sleep?
Red and near-infrared light therapy has been found to offer numerous benefits for improving sleep quality and regulating the sleep-wake cycle. One of the most significant benefits is the improvement of sleep duration and quality. Studies have shown that red and near-infrared light therapy may help support total sleep time, reduce feelings of sleepiness as well as the amount of time it takes to fall asleep, support the body’s biological clock, and potentially support sleep efficiency.
Red and near-infrared light therapy may also help people with some types of sleep problems, such as insomnia, in ways that are not specifically restricted to melatonin. Research shows that red light therapy can help to soothe feelings of tension and stress, for example. This may be able to help you fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer, even without considering the beneficial effects it has on melatonin.
Compared to other options and methods used for sleep, red and near-infrared light therapy is non-invasive and does not have the same side effects or the frequency of side effects that some of the other options have. Additionally, it may be more effective for some individuals who do not respond well to other methods.
Insufficient Red and Near Infrared Light Exposure
In modern times, we are exposed to significantly less red and near-infrared light than in previous periods of human history. This is due to several reasons:
- Decreased natural light exposure - Our modern lifestyles, with more time spent indoors and less exposure to bright light like sunlight, have led to a reduction in natural light exposure. This includes exposure to red and near-infrared light.
- Decreased indoor natural light - While time spent indoors has increased significantly in modern times, energy-efficient windows developed in recent decades have further limited exposure to natural light, even indoors. Many energy-efficient windows filter out near-infrared light.
- Increase in blue light exposure - Electronic devices such as smartphones and laptops emit a high amount of blue light. While this does not decrease exposure to red light, it can interfere with the production of melatonin and disrupt the sleep-wake cycle, making it difficult to achieve good sleep.
- Decreased exposure to firelight - Throughout most of human history, people spent a significant amount of time around fires, which emit red and near-infrared light. Modern lighting does not provide the same wavelength of light.
This reduced exposure to red and near-infrared light has led to a need for supplementation provided by red light therapy. Red light therapy devices have become increasingly popular in recent years as a safe and non-invasive way to support cellular function and promote healing.
Using Red Light Therapy to Support Melatonin Production
Red and near-infrared light therapy can be a powerful tool for improving sleep quality and supporting the body’s natural melatonin production. If you're interested in trying red light therapy at home, here are some tips to get you started:
- Position the device correctly - The light source should be positioned around 6-12 inches from the skin and directed towards the target area. When you are using red light therapy to support melatonin production, consider using a full-body system.
- Consider the time of day - While there is currently little research into how the time of day affects the results of red light therapy, it is logical to use it in the evening if you are trying to promote sleep. This is when exposure to natural red light is most important to regulate circadian melatonin production. “Start with shorter durations (around 10-15 minutes) and gradually increase as needed. Evening use is generally recommended, ideally one to two hours before bedtime. Avoid using blue-light emitting devices before sleep as they might suppress melatonin production when used too close to bedtime and negate your efforts from red light therapy,” notes Heidi Wright, Registered Nurse.
- Use a professional-grade device - Red and near-infrared light therapy devices should emit light at a wavelength of around 660-850 nanometers. Ensure that you are using a device that provides this wavelength range and has a high intensity of light that is able to cover a large area of your body. Most people who use red light therapy specifically to support melatonin production are using it for their sleep. Red light therapy has been shown to help support sleep and restfulness by potentially promoting healthy melatonin production and providing additional sleep-related benefits.
Remember, RLT is a complementary method, and results may vary. It likely works best when combined with good sleep hygiene practices like a regular sleep schedule and a relaxing bedtime routine.
Mito Red Light
At Mito Red Light, we are committed to providing you with the highest quality red light therapy at home products. Our products can help you achieve reliable doses of professional-grade red light therapy, optimizing the effect that red light and near-infrared light have on your melatonin production.
We provide a variety of red light therapy products that are specifically designed to provide the wavelengths of light used to improve melatonin production. We welcome you to review our selection of high-quality products or to contact one of our expert representatives at 1-866-861-6486 or 1-866-861-MITO.